Pediatric Orthopedic Surgery
Pediatric orthopedics is a Sub-specialty within orthopedic surgery that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of musculoskeletal conditions and injuries in infants, children, and young adults.
Pediatric orthopedic surgeons’ expertise in addressing a wide range of conditions, from congenital abnormalities to developmental and traumatic disorders. This field of orthopedics approaches multiple disciplines and often involves collaborating with medical specialists like pediatricians, physiotherapists, and occupational therapists, to modify the child’s individual needs. We as a Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon, not only do the surgery, but they also perform non-surgical procedures such as casting, bracing and advise on physical therapy and rehabilitation.
The scope of pediatric orthopedics is quite huge, but some of the conditions we commonly encounter in day to day practice are
Pediatric Orthopaedic Treatments
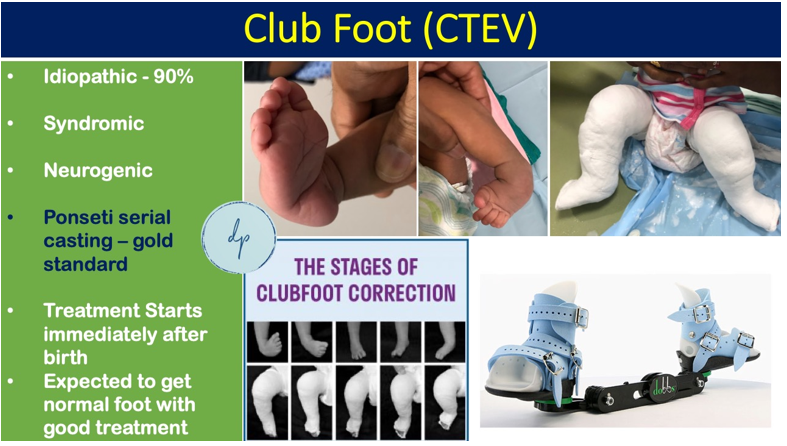
Clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus, is a congenital deformity characterized by the inward and downward twisting of the foot. Affecting approximately 1 in 1,000 newborns, this condition can vary in severity and often impacts both feet. The exact cause remains unclear, though genetic and environmental factors may contribute.
Early diagnosis, typically through physical examination and prenatal ultrasound, allows for prompt intervention. Treatment usually involves the Ponseti Method, a series of gentle manipulations and casting, followed by bracing to maintain correction. In more severe cases, surgery may be required.
With timely and appropriate treatment, most children with clubfoot can achieve normal foot function and lead active lives.
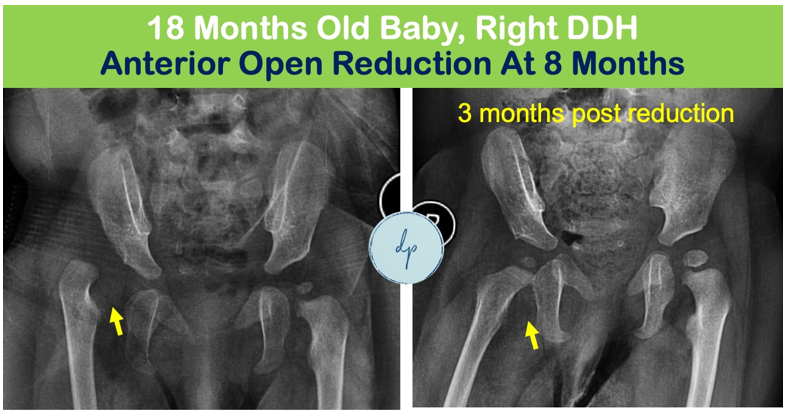
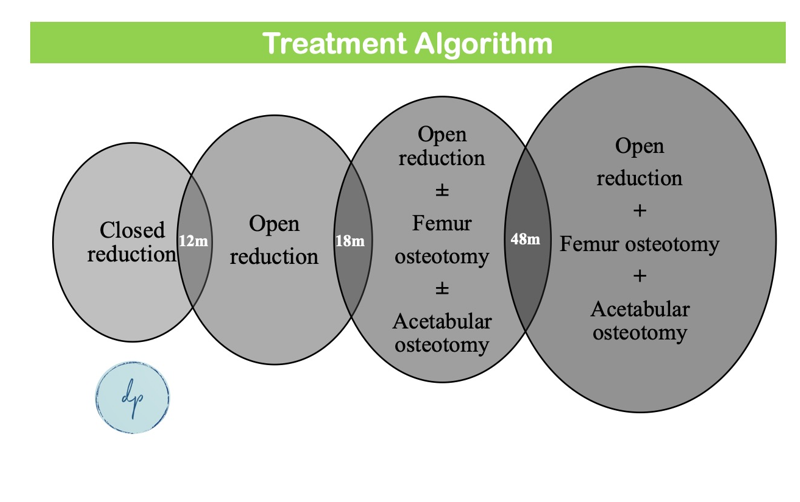
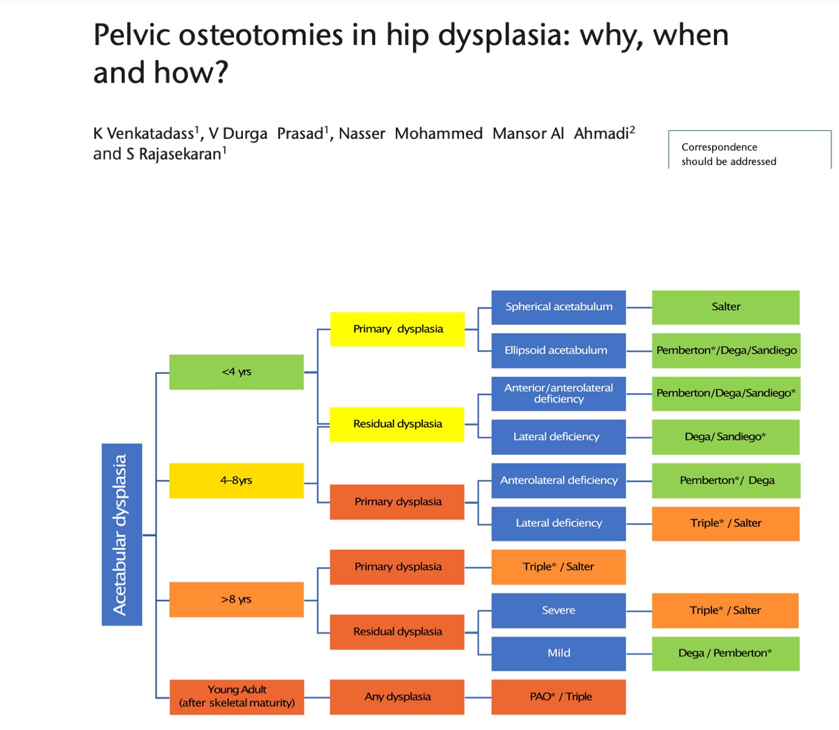
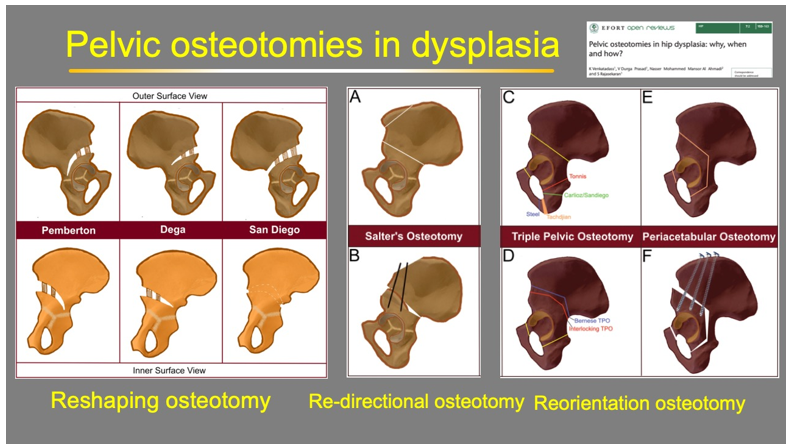
Hip dysplasia, or developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH), is a condition where the hip joint is improperly formed, leading to instability or dislocation. It affects approximately 1 in 1,000 newborns, with varying degrees of severity. Factors contributing to hip dysplasia include genetic predisposition, breech birth, and tight swaddling practices. Early detection through physical exams and ultrasound is crucial for effective treatment. Treatment options range from Pavlik Harnesses and braces for infants to surgical interventions for older children. Prompt and appropriate management can ensure normal hip development and function, allowing children to lead active, healthy lives.
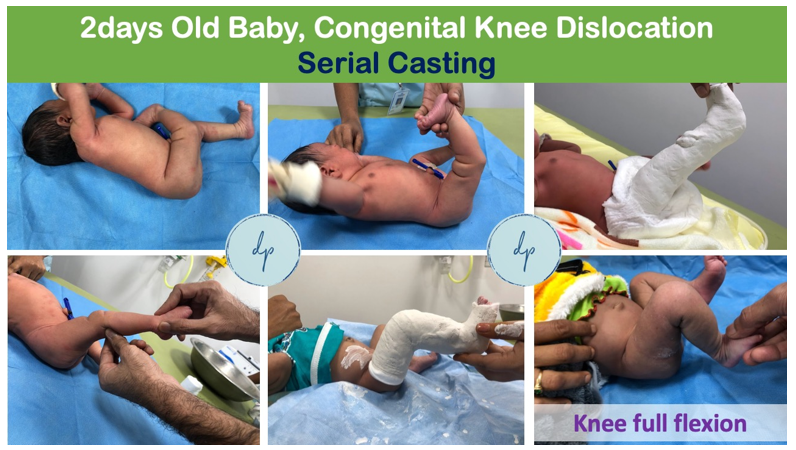
Congenital dislocation of the knee is a rare birth defect where the knee joint is abnormally positioned, often with the tibia displaced forward relative to the femur. This condition can be associated with other musculoskeletal anomalies such as hip dysplasia or clubfoot. Symptoms include an obvious deformity, limited knee movement, and difficulty with leg positioning. Early diagnosis through physical examination and imaging is crucial for effective treatment, which may include gentle manipulation, splinting, or casting in infancy, and surgical intervention in more severe cases. Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to ensure proper joint alignment and function, allowing for normal development and mobility.
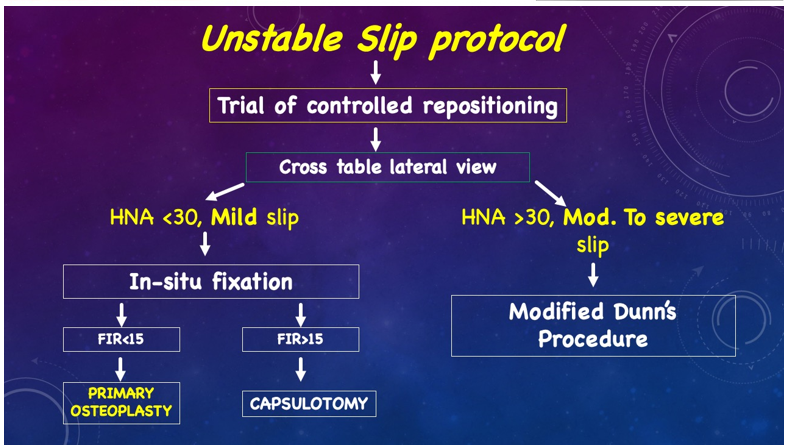
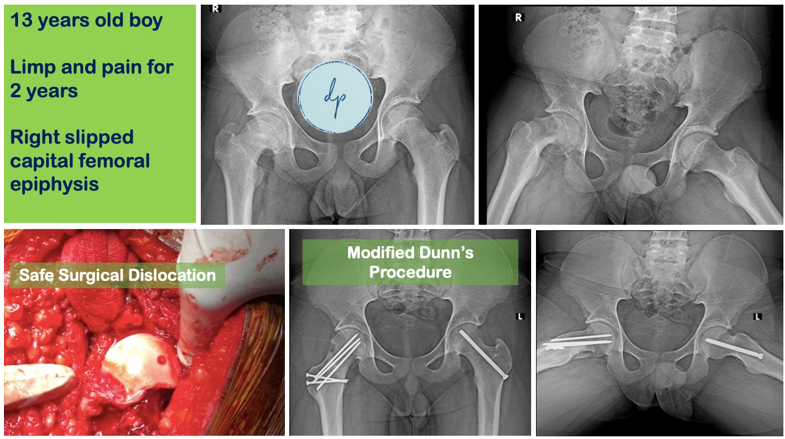
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) is a pediatric orthopedic condition where the femoral head slips off the neck of the femur at the growth plate. Commonly occurring during the adolescent growth spurt, SCFE typically affects children between 10 and 16 years old and is more prevalent in males and those with obesity or endocrine disorders. Symptoms include hip, thigh, or knee pain and a limp. Early diagnosis through physical examination and imaging, such as X-rays, is vital to prevent further slippage and complications. Treatment usually involves surgical intervention to stabilize the femoral head, commonly Insitu Pinning for mild cases and Modified Dunn’s Procedure for more severe cases. With timely and appropriate management, most children can recover well and maintain good hip function.
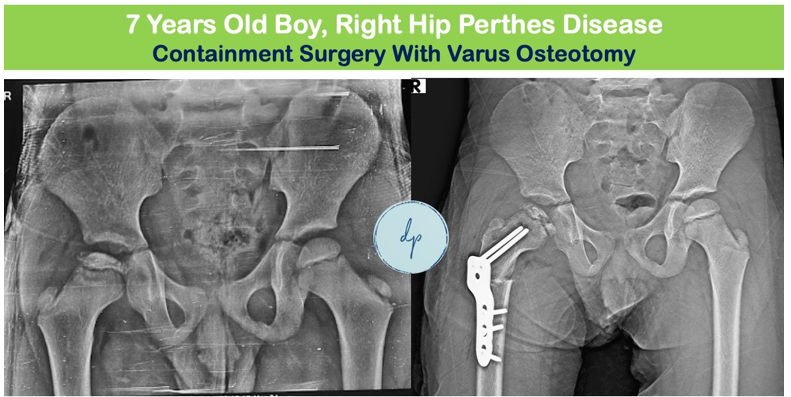
Perthes disease is a childhood condition where the blood supply to the femoral head (the ball part of the hip joint) is temporarily disrupted, causing the bone to weaken and eventually collapse. Affecting children between the ages of 4 and 10, Perthes disease is more common in boys than girls. Symptoms include limping, hip or groin pain, and limited range of motion in the hip. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI. Treatment aims to relieve pain, maintain hip motion, and ensure the femoral head re-forms properly, using methods ranging from physical therapy and bracing to surgical procedures (Containment Surgery) in severe cases. Early and appropriate intervention can lead to good long-term outcomes, allowing children to resume normal activities.
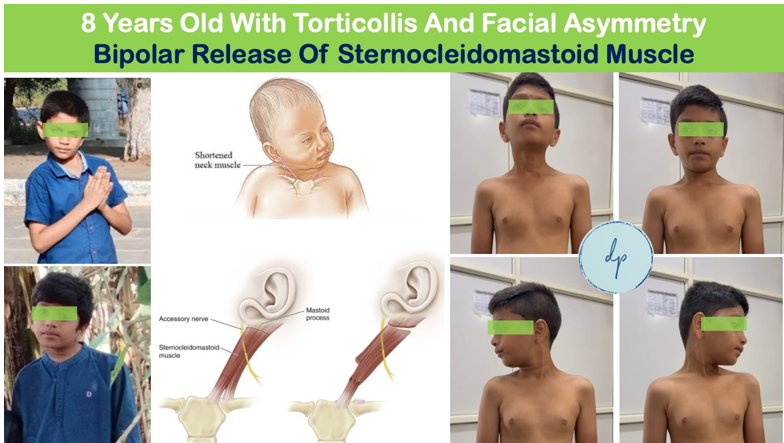
Congenital torticollis, is a condition present at birth where an infant's neck muscles are abnormally tight, causing the head to tilt to one side while the chin points to the opposite side. This condition is often due to the tightness of sternocleidomastoid muscle and can be associated with a birth injury or intrauterine positioning. Symptoms include a visible head tilt, difficulty turning the head, and sometimes a small, palpable lump in the affected muscle. Early diagnosis through physical examination is crucial, and treatment typically involves stretching exercises, physical therapy, and positioning techniques to improve muscle length and flexibility. In rare cases, surgical intervention (Bipolar or Monopolar Release) may be required. With prompt and consistent treatment, most infants with congenital torticollis achieve full range of motion and a normal head posture.
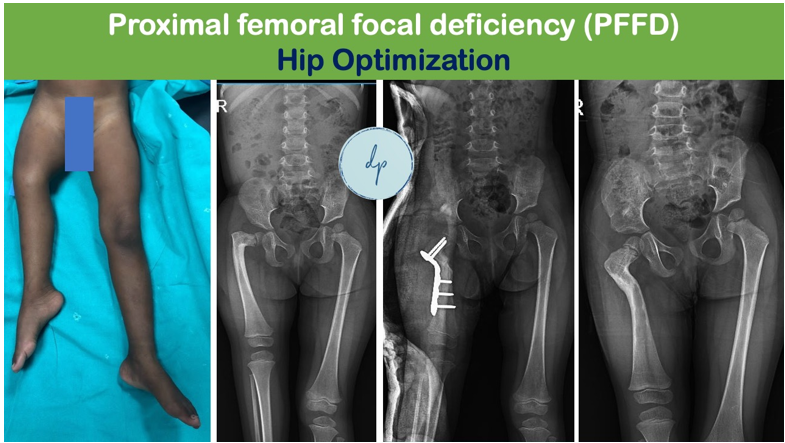
Congenital limb deficiencies are birth defects where an infant's limbs are partially or completely missing, or malformed. These deficiencies can occur in the upper or lower limbs and vary in severity, affecting one or more limbs. Causes include genetic mutations, environmental factors, or disruptions during fetal development, although many cases have no identifiable cause. Common conditions are Proximal Femoral Focal Deficiency (PFFD), Tibia and Fibular Hemimelia’s, Radial and Ulnar Club Hand. Symptoms range from minor deformities to significant functional impairments, impacting mobility and daily activities. Diagnosis is often made through prenatal ultrasound or physical examination at birth. Treatment options depend on the severity and include prosthetics, physical therapy, and sometimes surgical interventions to improve function and appearance. With comprehensive care and support, individuals with congenital limb deficiencies can achieve greater independence and lead active, fulfilling lives.
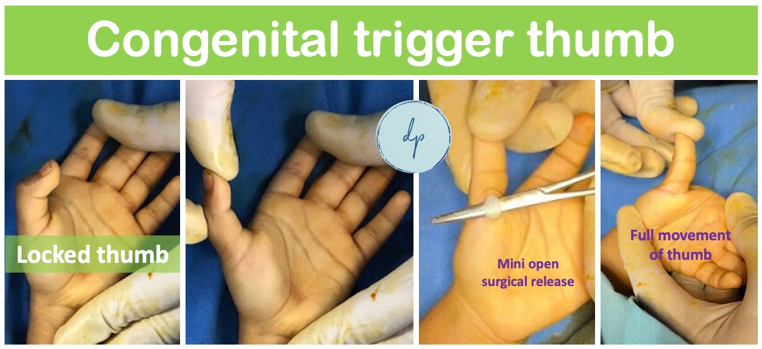
Pediatric hand deformities encompass a variety of congenital conditions affecting the structure and function of a child's hands. These deformities, which can include syndactyly (webbed fingers), polydactyly (extra fingers), and underdeveloped or missing fingers, often arise from genetic factors or developmental disruptions during pregnancy (constriction band syndrome). Symptoms and functional limitations vary, impacting the child's ability to grasp and manipulate objects. Early diagnosis through physical examination and imaging is crucial for planning treatment, which may involve surgical correction, occupational therapy, and the use of adaptive devices. With timely and appropriate intervention, many children with hand deformities can improve their hand function and participate fully in daily activities.
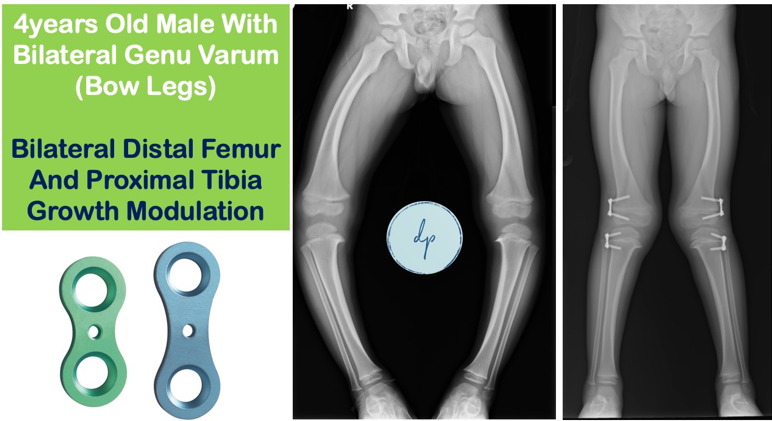
Pediatric genu varum (bowlegs) and genu valgum (knock-knees) are common conditions affecting the alignment of a child's legs. Genu varum causes the legs to bow outward, while genu valgum results in the knees angling inward. Both conditions are often part of normal growth and development, typically self-correcting with age. However, severe or persistent cases may require medical evaluation. Diagnosis involves physical examination, blood investigations (metabolic profile) and radiographs. Treatment options range from observation, corrective braces and surgical interventions like Growth Modulation and Corrective Osteotomies. Early intervention can ensure proper leg alignment, preventing future complications.
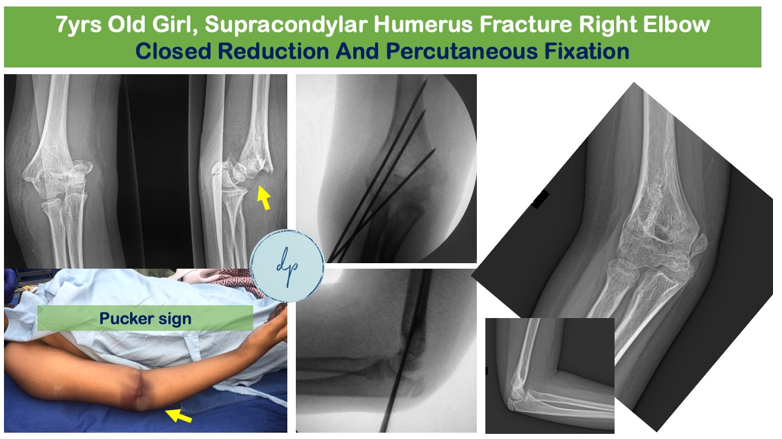
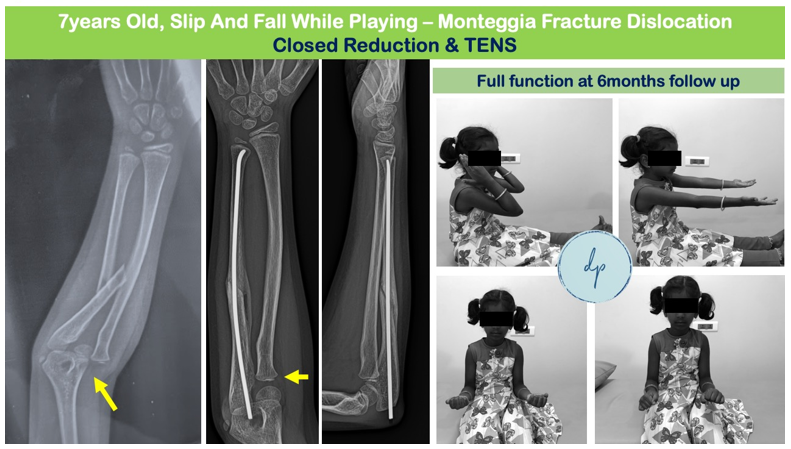
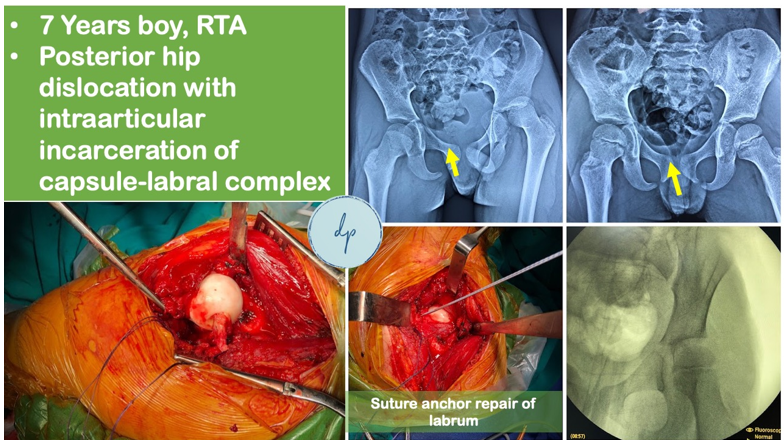
Pediatric fractures are common injuries in children, often resulting from falls, sports activities, or accidents. Due to their growing bones, children are susceptible to unique fracture patterns, such as greenstick or growth plate fractures. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and inability to move the affected limb. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and imaging, such as X-rays. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the fracture and may include casting, splinting, or surgical intervention. Children's bones generally heal faster than adults, but proper care and follow-up are essential to ensure correct alignment and prevent future growth issues. With appropriate treatment, most pediatric fractures heal completely, allowing children to return to their regular activities.
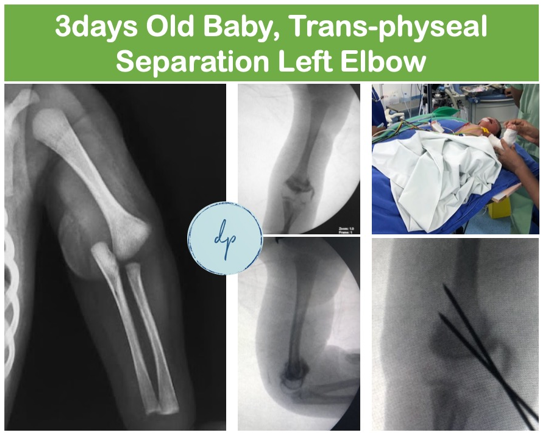
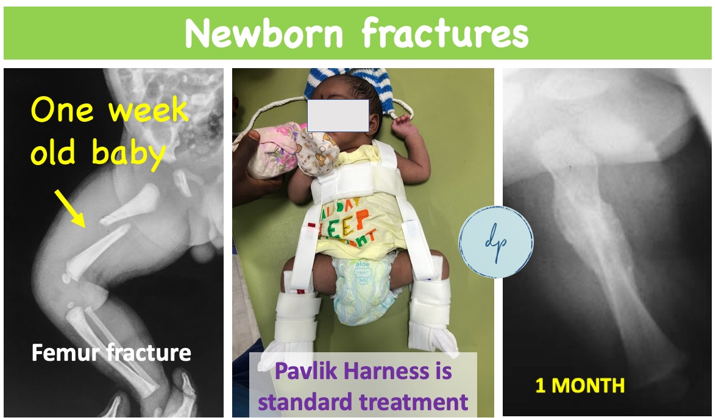
Newborn fractures are injuries that occur during or shortly after birth, often resulting from the delivery process. Common types include Clavicle Fractures and, less frequently, fractures of the Humerus or Femur. Symptoms may include limited movement or swelling in the affected area. Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination and imaging, such as X-rays. Treatment generally involves gentle handling and supportive care, as these fractures often heal on their own with minimal intervention.
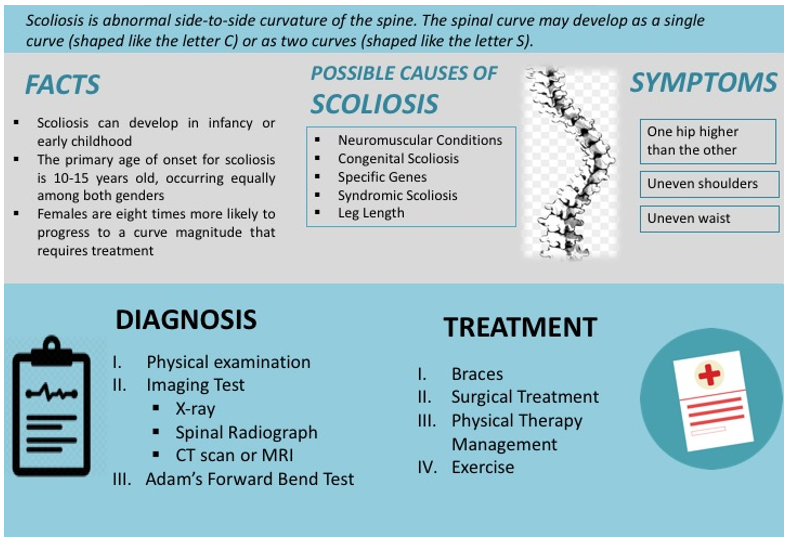
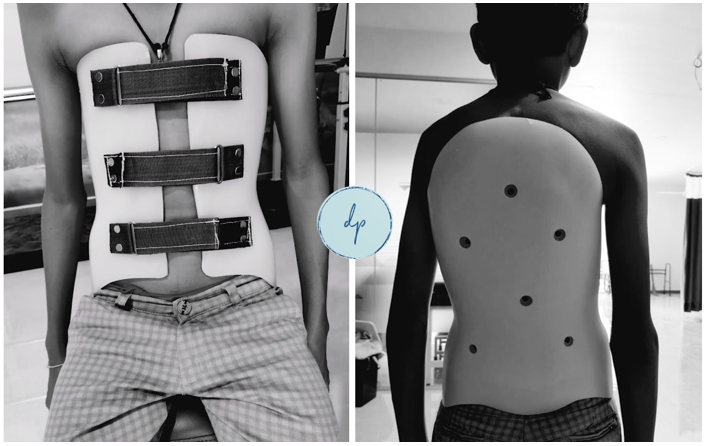
Scoliosis and spinal deformities involve abnormal curvature of the spine that can affect posture and overall function. Scoliosis is characterized by a sideways curve, often shaped like an "S" or "C," while other spinal deformities may include kyphosis (excessive forward rounding) or lordosis (excessive inward curvature). These conditions can develop during adolescence or as a result of congenital issues or neuromuscular conditions. Diagnosis is typically made through physical examination and imaging studies such as X-rays. Treatment options vary based on the severity and may include observation, physical therapy, bracing, or, in severe cases, surgical intervention. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to manage symptoms, prevent progression, and support healthy spine development.
Pediatric limb length discrepancy occurs when one limb is shorter or longer than the other, which can result from congenital conditions, growth disturbances, or trauma. This condition can affect a child's gait, posture, and overall mobility. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and imaging studies to determine the extent and cause of the discrepancy. Treatment options depend on the severity and underlying cause and may include observation, orthotic devices, or surgical interventions such as Growth Modulation or lengthening procedures with Ilizarov methods or LRS system. Early diagnosis and management are essential to address any functional issues and support balanced growth and development.
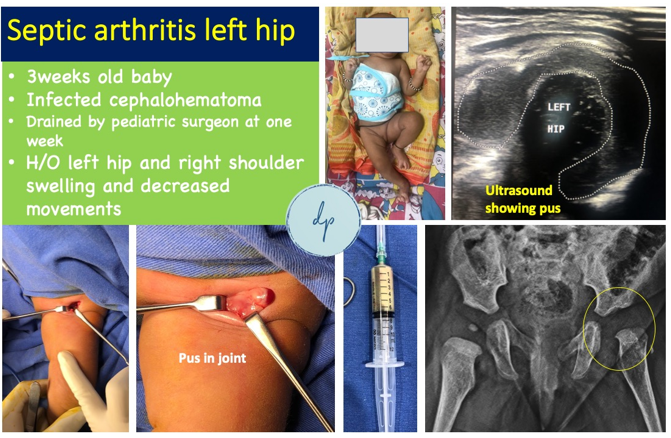
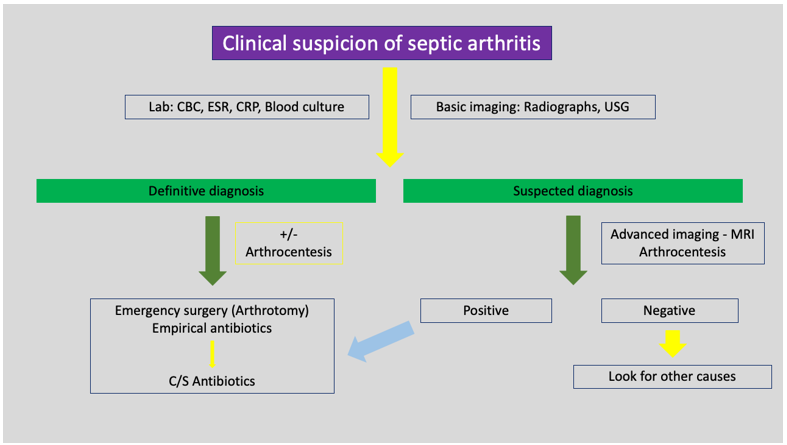
Pediatric orthopedic infections are infections affecting the bones, joints, or surrounding soft tissues in children. Common types include Osteomyelitis (infection of the bone) and Septic Arthritis (infection of the joint). These infections can result from bacterial entry through an injury or spread from another infection. Symptoms often include localized pain, swelling, limp, and fever. Diagnosis involves clinical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Treatment typically includes antibiotics to combat the infection and usually requires surgical intervention to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue. Early and effective treatment is crucial to prevent long-term complications and support optimal recovery and joint function.
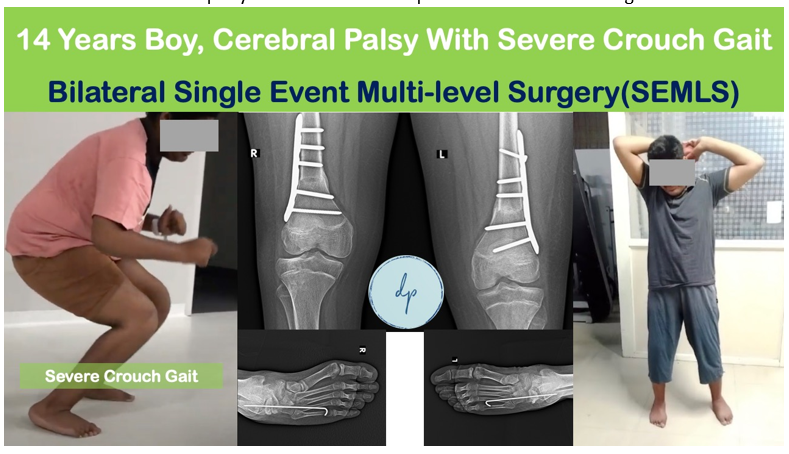
Cerebral palsy is a group of neurological disorders that affect movement, muscle tone, and posture due to brain damage occurring before or during birth. It can result in difficulties with motor skills, coordination, and balance, and may be accompanied by other conditions such as intellectual disabilities or seizures. Symptoms vary widely in severity and may include muscle stiffness, weakness, and involuntary movements. Diagnosis is made through a combination of clinical evaluation and imaging studies. While there is no cure, treatment focuses on managing symptoms and improving quality of life through physical therapy, medication, and, in some cases, surgery (Single Event Multi-level Surgeries – SEMLS). Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach can help individuals with cerebral palsy achieve their fullest potential and lead fulfilling lives.
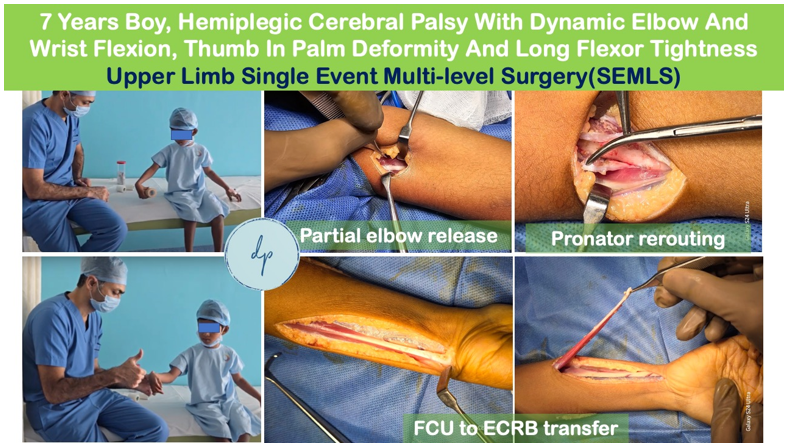
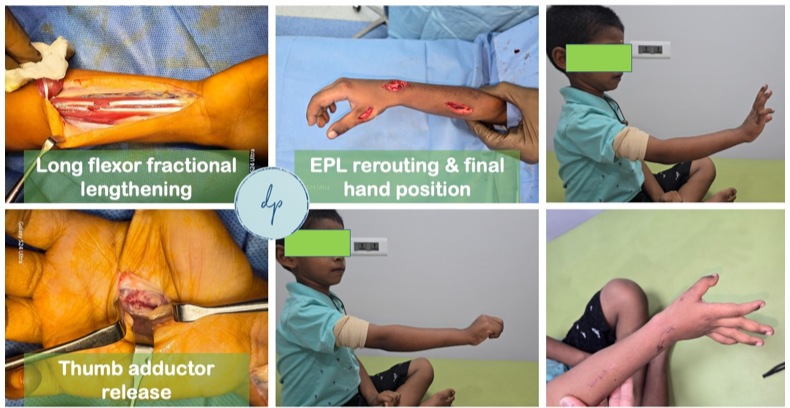
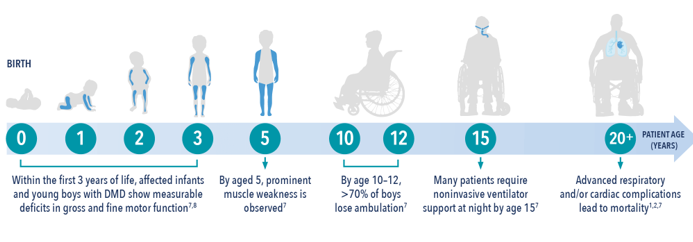
Pediatric neuromuscular disorders are a group of conditions affecting the nerves and muscles, leading to weakness, impaired movement, and developmental delays. These disorders, which include conditions like Muscular Dystrophy, Spinal Muscular Atrophy, and Peripheral Neuropathies, can significantly impact a child's physical abilities and overall quality of life. Diagnosis involves a thorough clinical evaluation, genetic testing, and imaging studies. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, improving function, and supporting the child’s development through physical therapy, medications, and sometimes surgical interventions. Early intervention and a comprehensive care approach are crucial to maximize the child's potential and enhance their quality of life.

Pediatric sports injuries are injuries sustained by children and adolescents during athletic activities. Common injuries include sprains, strains, fractures, and concussions. These injuries can result from acute trauma, overuse, or improper technique. Symptoms vary depending on the injury but often include pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination and imaging studies like X-rays or MRIs. Treatment ranges from rest and physical therapy to surgical intervention in severe cases. Prompt and appropriate management is essential to ensure proper healing, prevent recurrence, and enable young athletes to safely return to their sports activities.